What Is The Fourth Trimester Of Pregnancy?

Pregnancy is typically divided into thirds based on fetal development. The first trimester of pregnancy begins at the beginning of a woman’s last menstrual period and continues until the beginning of the 14th week of pregnancy. During that time, all the important organs and structures of the fetus develop. During the second trimester of pregnancy, which lasts until the 28th week of pregnancy, the fetus grows and matures rapidly. The third trimester of pregnancy lasts from the 29th week of pregnancy to delivery, during which the fetus reaches viability outside the womb. So what is the fourth trimester of pregnancy?
The first three months of a baby’s life have traditionally been called the baby’s bedtime, but some call this stage the fourth trimester of pregnancy. Being born into a cold and unknown world is a huge upheaval for a baby, and getting used to it takes time. When parents keep in mind how difficult it is for a child to adjust to life outside the womb, it is easier for them to adapt to the situation and the needs of the baby.
What is the fourth trimester of pregnancy?
The fourth trimester of pregnancy is a term developed by American pediatrician Harvey Karp. According to Carp’s theory, a person has certain conditions to survive at birth, but he cannot do it without help. Fundamental survival abilities continue to develop for months after birth.
For example, many mammalian pups are able to walk immediately after birth, and although they also need the care of their mothers for a long time, they are considerably more willing than human children to survive in the world. We humans are dependent on the care of our parents for years after we were born. This gave rise to the theory of the fourth trimester of pregnancy, according to which all babies – including those born full-time – are still immature at the time of birth. In order for the nervous system to develop fully, the fetus would have to live longer in the mother’s womb. According to Karp, it is for this reason that the first months of a baby’s life should be considered as one stage of pregnancy.
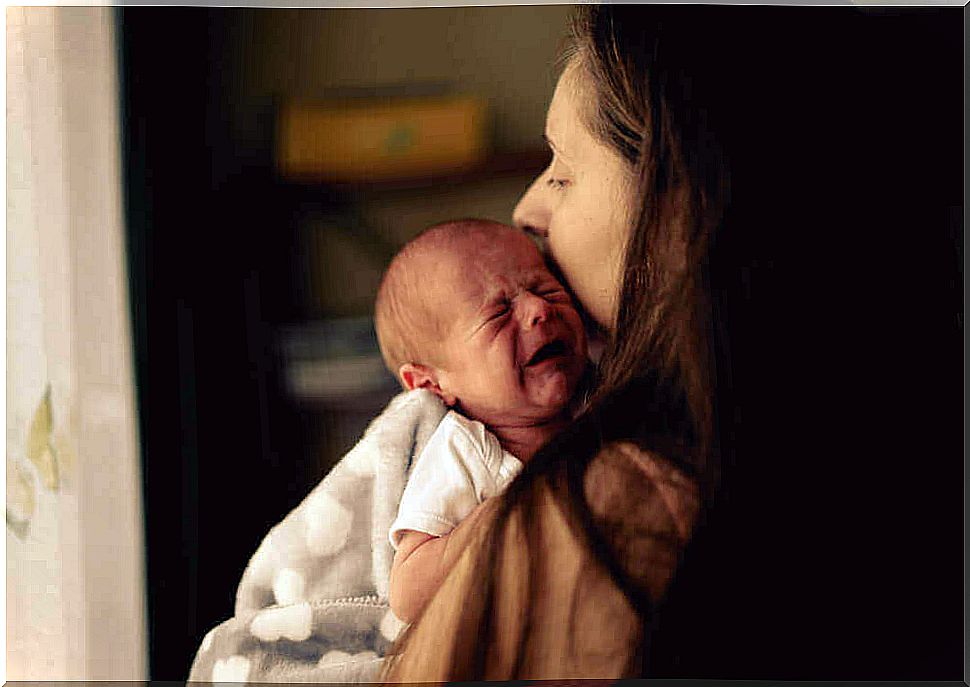

A difficult change for the baby
During the first months of life, the baby may suffer from feelings of anxiety, sleep problems and seizures, for example. Such problems are not at all unusual, but on the contrary surprisingly common. The baby’s living environment has changed completely differently from what she experienced during her first nine months of development in her mother’s womb.
- Inside the uterus, the temperature is constantly around 37 degrees, while in the outside world, the temperature is considerably lower and varies drastically from time to time.
- In the womb, the life of the fetus is very smooth, and the stimuli it encounters are minor. After birth, the baby is exposed to a variety of odors, sounds, and visual stimuli, among other things.
- During pregnancy, the fetus receives the food, shelter, and intimacy it needs from its mother, and it does not have to feel hunger, thirst, or other unpleasant sensations. Such feelings, on the other hand, belong to the outside world, and it takes time for the baby to get used to them.
- The fetus growing in the womb is in constant contact with its mother. For the first time since birth, the baby feels loneliness and even fear when the mother is no longer constantly present.
How to deal with the fourth trimester of pregnancy?
Given the information listed above, parents should treat the fourth trimester of pregnancy as if it were one of the later stages of pregnancy. They should think about it so that the baby should not have to adjust to the world around him immediately after birth, but should be allowed to start his life in conditions as similar as possible to what he is used to inside the womb.
Such a soft decline in life is ensured by keeping the baby in great contact with the skin and providing him with food whenever he wishes. Continuous exposure of the baby to various stimuli should also be avoided. Holding in her arms and the voice of the parent restore the child to the safe and comfortable feeling he or she lost when entering the world.