Premature Baby Nutrition
Premature babies require special care, and the nutrition of the preterm baby plays a particularly important role in this. Proper nutrition allows a premature baby to continue growing at the same rate as if it were still living in the womb.
How is premature infancy defined?
Preterm refers to a child born before the 37th week of pregnancy.
The preterm infant can be further divided into subcategories:
- Extremely premature preterm:
A baby is born before the 28th week of pregnancy - A truly premature premature baby:
A baby is born before 28-32. weeks of pregnancy - Moderately premature preterm:
The baby was born before 32.-34. weeks of pregnancy - Late preterm preterm:
A baby is born before 34-37. weeks of pregnancy
The right kind of nutrition for a premature baby
The U.S. Academy of Pediatrics’s Nutrition Science Committee provides a definition of proper nutrition for premature babies. According to the committee, the right kind of nutrition for a premature baby is one that allows the premature baby to grow in line with what the baby would grow while in the womb. Diet should not burden the metabolic and defecation functions of the premature baby that have not yet developed.
A baby born prematurely 34-37. during pregnancy, it is still difficult to eat the breast or suck food from the baby bottle. This is due to the difficulty of sucking, breathing and swallowing a premature baby.
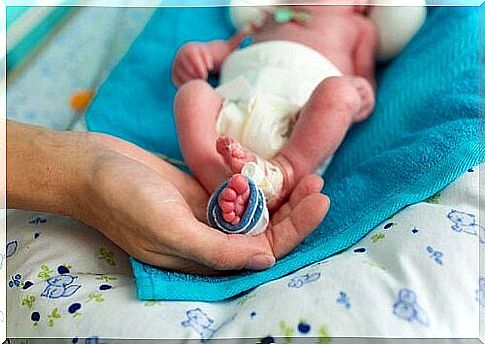
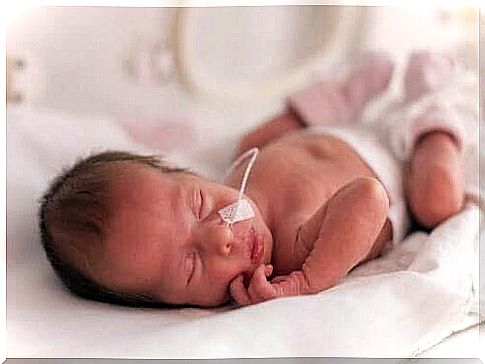
Because of this, a premature baby may need to be given the necessary nutrition intravenously. As a premature baby becomes stronger, the baby may begin to receive breast milk or breast milk substitute through a nasogastric tube.
The doctor inserts a nasogastric tube from the baby’s nose or mouth into the stomach. The amount of milk is increased very slowly, especially in the case of a very premature baby. This lowers the risk of the premature baby getting an intestinal inflammation called necrotizing enterocolitis.
Mother’s breast milk
The newborn’s stomach digests the mother’s breast milk best. A premature baby can get it faster through the tube and to a lesser extent compared to an artificial infant formula. Breast milk has a lower osmolality, is specifically intended for humans, and contains important properties useful for the defense system. Breast milk is one possible factor in the fight against neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis.
In addition, studies show that feeding a breast-fed premature baby with breast milk reduces the baby’s risk of developing nosocomial infections. Being in constant skin contact with the mother is also called kangaroo treatment. A premature baby should be treated for kangaroo as soon as medically possible, and treatment should be continuous and last as long as possible.
Maternal skin secretes a specific immunoglobulin A against bacteria that interact with similar antibodies in the newborn. In this way, the baby can be protected from bacteria that cause nosocomial infections.
The composition of breast milk
The composition of breast milk depends on whether the baby is born prematurely or full-time. During the first 24 weeks of pregnancy, the mother of a premature baby produces milk whose composition adapts to the baby’s nutritional needs. Breast milk is only slightly deficient in calcium and phosphorus.
When a premature baby reaches the age of 4-6 weeks, she should receive supplemental nutrition in addition to breast milk. At this age, the baby is mature enough to get the minerals and proteins contained in the supplement.
In addition, the supplement contains calcium and phosphorus. This minimizes the low bone density as well as the biochemical rice disease that can occur in premature babies during the first weeks of life that receive breast milk.
The milk produced by the mother of a premature baby contains a variety of amino acids that are essential for the baby’s developing central nervous system. Because breast milk is rich in a variety of nutrients, it is considered important for the baby’s defense system.
Breast milk also contains medium and long chain fatty acids, which are important for brain function. Milk contains more cholesterol than breast milk produced by the mother of an adult baby, as well as breast milk substitutes.
Other important factors related to the nutrition of a premature baby
Particular care must be taken to obtain the fluid of a premature baby, as it is more difficult for the premature baby to maintain the correct fluid balance. A premature baby is very prone to dehydration, but also to over-hydration.
Some premature babies have to continue to take supplemental food even after leaving the hospital. For a breastfed baby, this can mean one or two bottles of fortified breast milk a day, as well as iron and vitamin D supplements.
Some premature babies need more supplements than others. Some premature babies are unable to eat enough milk to get the calories they need to grow properly.