Chronic Urticaria In Children
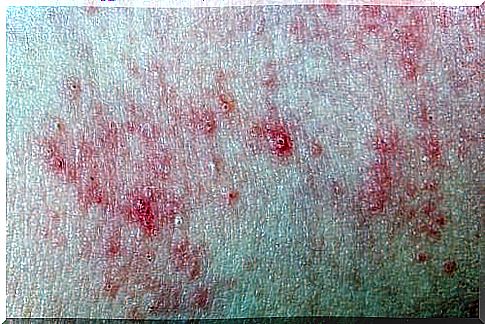
Urticaria, or urticaria, normally lasts for a few hours or up to a few days. Prolonged, chronic urticaria is referred to as symptoms lasting more than six weeks. Today we will talk about what causes chronic urticaria in children, how it is diagnosed and how it is treated.
Urticaria is a condition that affects the epidermis, the outer layer of the skin. Symptoms include red and itchy bumps or patches resembling nettle burns. Bangs occur either apart or in a cluster and can spread to even a large part of the body. Thus, urticaria may be limited to a small area of skin or spread to the entire arm, for example.
Chronic urticaria in children is often due to an allergic reaction. In other words, the irritation characteristic of the disorder is the body’s reaction to allergens. Chronic urticaria is an itchy and unpleasant discomfort that should be closely monitored by parents until recovery.
Causes of chronic urticaria in children
Chronic urticaria is most often caused by autoimmune urticaria or urticaria triggered by a physical stimulus. Outbreaks are caused by histamine released by the body’s mast cells. Activation of mast cells causes small blood vessels under the skin to open, causing fluid to accumulate on the skin, causing bumps and blemishes. The exact cause of the reaction can be difficult to determine. Many things can cause hives, and each body reacts in its own way. Thus, in many cases, it is difficult to determine the root cause of a child’s hives.
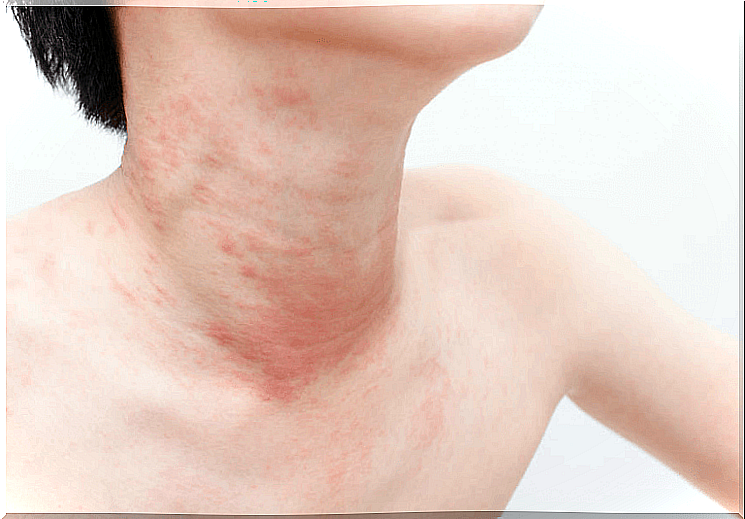
Common causes of chronic urticaria are:
- Autoimmune diseases
- Insect stings
- Drug side effects
- Food allergies
Symptoms of chronic urticaria in children
The most obvious and visible symptom of chronic urticaria in children are red and itchy bumps or patches resembling hives. Bangs can be isolated or occur in a cluster. The location, shape, and size of the rash can vary from hour to hour. Symptoms of chronic urticaria most often occur daily and worsen from time to time. Some patients also experience deeper swelling of the skin and mucous membranes.
In severe cases, swelling can affect the throat, causing the following problems:
- Fatigue
- Breathing difficulties
- Loss of consciousness due to an anaphylactic reaction
How is chronic urticaria in children diagnosed?
Diagnosing acute urticaria is usually easy, as no other disease has as rapidly rising and disappearing bites. Diagnosing a chronic form of the disease and finding the causes of the disorder, on the other hand, is often much more difficult.

Extensive studies, such as allergy studies, are rarely helpful in diagnosing chronic urticaria. Diagnosis is usually based on the course and symptom history described by the patient’s parents. The only way to diagnose chronic urticaria is to rule out other possible diseases. To find out the cause of the discomfort, your doctor may ask your parents to keep a diary of the food your child eats and drinks.
Treatment of chronic urticaria in children
Mild cases heal on their own and do not require special treatment. In the case of chronic urticaria, it is important to determine the cause of the rash. When a child suffers from a severe rash, the doctor prescribes antihistamines that limit the release of histamine into the bloodstream, which in turn helps reduce skin irritation. In chronic urticaria, the effectiveness of antihistamines varies and they are not effective for possible edema.
Prescription drugs, such as oral cortisone, are sometimes used for very severe symptoms. In the case of physical urticaria, it is important to protect yourself from the triggers of the problem. The child should never be treated without a doctor’s advice.
If a child suffers from the symptoms of hives, it is important for parents to stay calm and not worry. As with many other skin problems, the use of creams and homemade herbs can be harmful. The most important thing is to talk to a doctor who knows how to instruct the best possible treatment for your child.









